UnrealPython基础学习
🛎 在 UE4 中使用 Python 开发入门。
视频学习链接:虚幻引擎使用Python开发
L1 在 UE4 中配置 Python
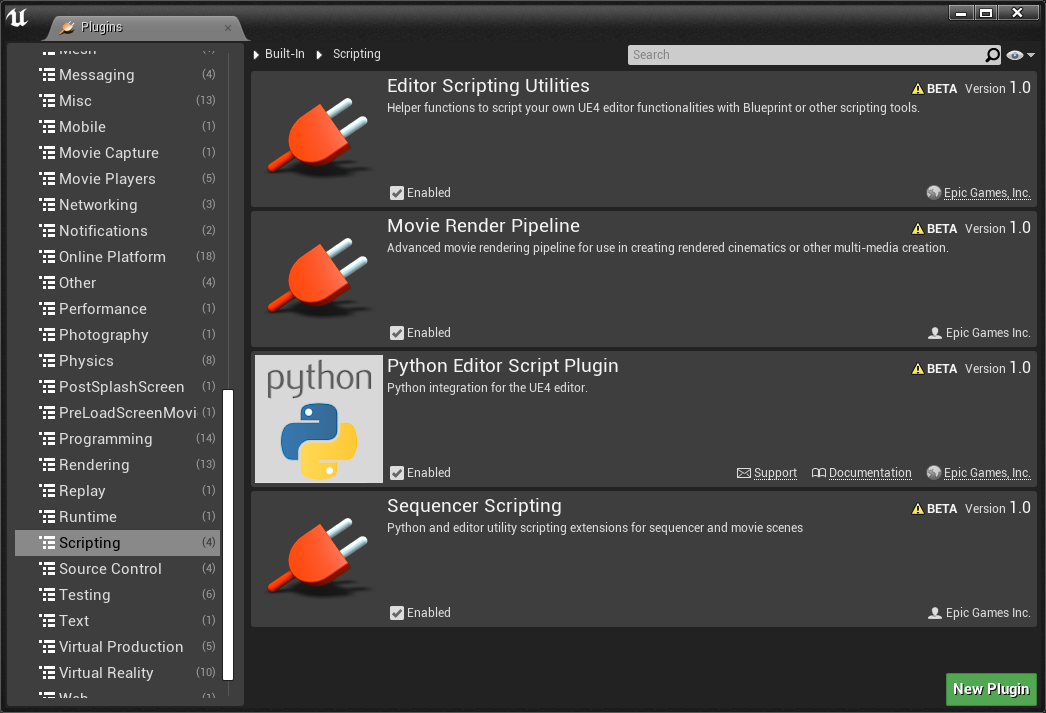
加载插件
从菜单 “Edit - Plugins” 进入插件管理,从左侧列表找到 “Scripting”。勾选 Python Editor Script Plugin 后重启引擎。
配置路径
从菜单 “Edit - Project Settings” 进入项目设置,从左侧列表找到 “Python”。
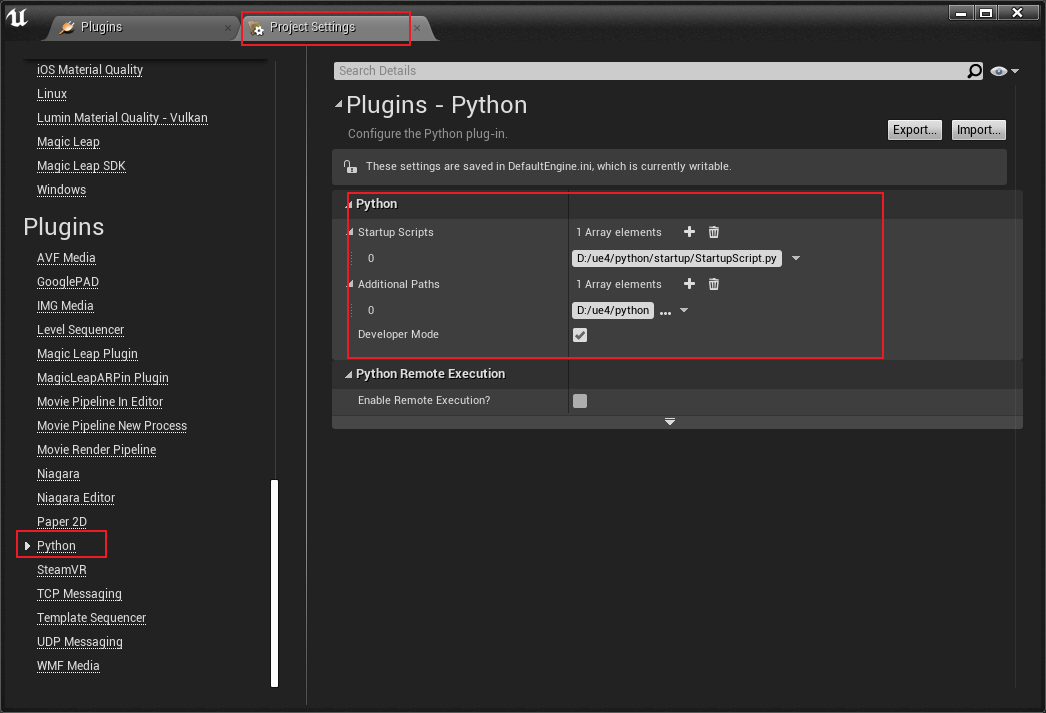
- Startup Scripts: 指定 UE4 打开时运行的脚本文件。
- Additional Paths: UE4 可以读取到 Python 脚本的路径。
Unreal Python API
Unreal Python API 文档
L2 使用 Python 导入资产
Example1 导入贴图和音频
AssetFunction_1.py
# coding: utf-8
import os
import unreal
# import AssetFunction_1 as af
# reload(af)
# af.importMyAssets()
asset_folder = 'D:/ue4/test/asset'
texture_jpg = os.path.join(asset_folder, 'dear.jpg').replace('\\','/')
sound_mp3 = os.path.join(asset_folder, 'easy.mp3').replace('\\','/')
def importMyAssets():
texture_task = bulidImportTask(texture_jpg, '/Game/MyAsset/Textures')
sound_task = bulidImportTask(sound_mp3, '/Game/MyAsset/Sounds')
executeImportTasks([texture_task, sound_task])
# ! 设置导入资产属性
def bulidImportTask(filename, destination_path):
task = unreal.AssetImportTask()
task.set_editor_property('automated', True)
task.set_editor_property('destination_name', '')
task.set_editor_property('destination_path', destination_path)
task.set_editor_property('filename', filename)
task.set_editor_property('replace_existing', True)
task.set_editor_property('save', True)
return task
def executeImportTasks(tasks):
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().import_asset_tasks(tasks)
for task in tasks:
for path in task.get_editor_property('imported_object_paths'):
print 'Imported {}'.format(path)Example2 导入fbx
AssetFunction_2.py
# coding: utf-8
import os
import unreal
# import AssetFunction_2 as af
# reload(af)
# af.importMyAssets()
asset_folder = 'D:/ue4/test/asset'
static_mesh_fbx = os.path.join(asset_folder, 'static_fbx.fbx').replace('\\','/')
skeletal_mesh_fbx = os.path.join(asset_folder, 'skeletal_fbx.fbx').replace('\\','/')
def importMyAssets():
# ! 静态网格
static_mesh_task = bulidImportTask(static_mesh_fbx, '/Game/MyAsset/StaticMeshes', buildStaticMeshImportOptions())
# ! 带骨骼的网格
skeletal_mesh_task = bulidImportTask(skeletal_mesh_fbx, '/Game/MyAsset/SkeletalMeshes', buildSkeletalMeshImportOptions())
executeImportTasks([static_mesh_task, skeletal_mesh_task])
def bulidImportTask(filename, destination_path, options=None):
task = unreal.AssetImportTask()
task.set_editor_property('automated', True)
task.set_editor_property('destination_name', '')
task.set_editor_property('destination_path', destination_path)
task.set_editor_property('filename', filename)
task.set_editor_property('replace_existing', True)
task.set_editor_property('save', True)
task.set_editor_property('options', options)
return task
def executeImportTasks(tasks):
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().import_asset_tasks(tasks)
for task in tasks:
for path in task.get_editor_property('imported_object_paths'):
print 'Imported {}'.format(path)
def buildStaticMeshImportOptions():
options = unreal.FbxImportUI()
# unreal.FbxImportUI
options.set_editor_property('import_mesh', True)
options.set_editor_property('import_textures', False)
options.set_editor_property('import_materials', True)
options.set_editor_property('import_as_skeletal', False) # Static Mesh
# unreal.FbxMeshImportData
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_translation', unreal.Vector(50.0, 0.0, 0.0))
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_rotation', unreal.Rotator(0.0, 110.0, 0.0))
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_uniform_scale', 1.0)
# unreal.FbxStaticMeshImportData
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('combine_meshes', True)
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('generate_lightmap_u_vs', True)
options.static_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('auto_generate_collision', True)
return options
def buildSkeletalMeshImportOptions():
options = unreal.FbxImportUI()
# unreal.FbxImportUI
options.set_editor_property('import_mesh', True)
options.set_editor_property('import_textures', True)
options.set_editor_property('import_materials', True)
options.set_editor_property('import_as_skeletal', True) # Skeletal Mesh
# unreal.FbxMeshImportData
options.skeletal_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_translation', unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
options.skeletal_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_rotation', unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, 0.0))
options.skeletal_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_uniform_scale', 1.0)
# unreal.FbxSkeletalMeshImportData
options.skeletal_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('import_morph_targets', True)
options.skeletal_mesh_import_data.set_editor_property('update_skeleton_reference_pose', False)
return optionsExample3 创建、复制、删除、重命名资产和文件夹
AssetFunction_3.py
# coding: utf-8
import os
import unreal
# import AssetFunction_3 as af
# reload(af)
# af.createDirectory()
# ! 创建文件夹 ~/MyNewDirectory
def createDirectory():
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.make_directory('/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory')
# ! 复制文件夹 ~/MyNewDirectory -> ~/MyNewDirectory_Duplicated
def duplicateDirectory():
return unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.duplicate_directory('/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory', '/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory_Duplicated')
# ! 删除文件夹 ~/MyNewDirectory
def deleteDirectory():
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.delete_directory('/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory')
# ! 重命名文件夹 ~/MyNewDirectory_Duplicated -> ~/MyNewDirectory_Renamed
def renameDirectory():
return unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.rename_directory('/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory_Duplicated', '/Game/MyAsset/MyNewDirectory_Renamed')
# ! 复制资产 ~/dear -> ~/dear_Duplicated
def duplicateAsset():
return unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.duplicate_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Duplicated')
# ! 删除资产 ~/dear
def deleteAsset():
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.delete_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear')
# ! 判断资产是否存在
def assetExist():
print unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.does_asset_exist('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear')
print unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.does_asset_exist('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Duplicated')
# ! 重命名资产 ~/dear_Duplicated -> ~/dear_Renamed
def renameAsset():
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.rename_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Duplicated', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Renamed')
# ! 显示复制资产提示框 ~/dear_Renamed -> ~/dear_Duplicated
def duplicateAssetDialog(show_dialog=True):
if show_dialog:
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().duplicate_asset_with_dialog('dear_Duplicated', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures', unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Renamed'))
else:
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().duplicate_asset('dear_Duplicated', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures', unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Renamed'))
# ! 显示重命名提示框
# ! ~/dear_Renamed -> ~/dear_Renamed_2
# ! ~/dear_Duplicated -> ~/dear_Duplicated_Renamed
def renameAssetDialog(show_dialog=True):
first_renmae_data = unreal.AssetRenameData(unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Renamed'), '/Game/MyAsset/Textures', 'dear_Renamed_2')
second_rename_data = unreal.AssetRenameData(unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear_Duplicated'), '/Game/MyAsset/Textures', 'dear_Duplicated_Renamed')
if show_dialog:
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().rename_assets_with_dialog([first_renmae_data, second_rename_data])
else:
unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().rename_assets([first_renmae_data, second_rename_data])L3 使用 Python 调用 C++ 函数
可以通过公开蓝图类的方式使 Python 可以访问 C++ 的函数。
创建蓝图C++类
- 首先,创建一个继承蓝图函数库的C++类,命名为“ ZFunction ”,创建成功后会自动打开 Visual Studio。
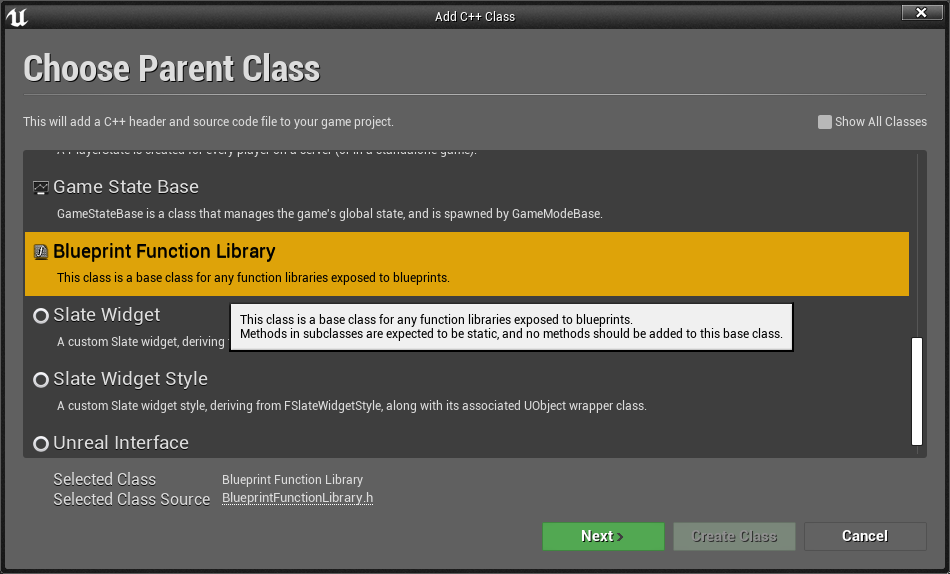
- 修改 .h 文件
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #pragma once #include "CoreMinimal.h" #include "Kismet/BlueprintFunctionLibrary.h" #include "ZFunction.generated.h" /** * */ UCLASS() class SCRIPT_PROJ_API UZFunction : public UBlueprintFunctionLibrary { GENERATED_BODY() public: UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable) static void CalledFromPython(FString InputString); }; - 修改 .cpp 文件
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #include "ZFunction.h" void UZFunction::CalledFromPython(FString InputString) { UE_LOG(LogTemp, Error, TEXT("%s"), *InputString); }遍历函数和类
查看 UE4 中所有函数和类:查看类中所含方法,可以看到我们创建的 ‘called_from_python’ 方法在其中。for x in sorted(dir(unreal)): print xfor x in sorted(dir(unreal.ZFunction)): print x
调用 C++ 方法
unreal.ZFunction.called_from_python('haha')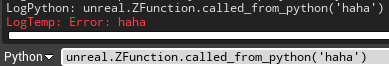
L4 修改文件夹颜色
定义类和方法
- 创建一个继承蓝图函数库的C++类,命名为“ CppLib ”
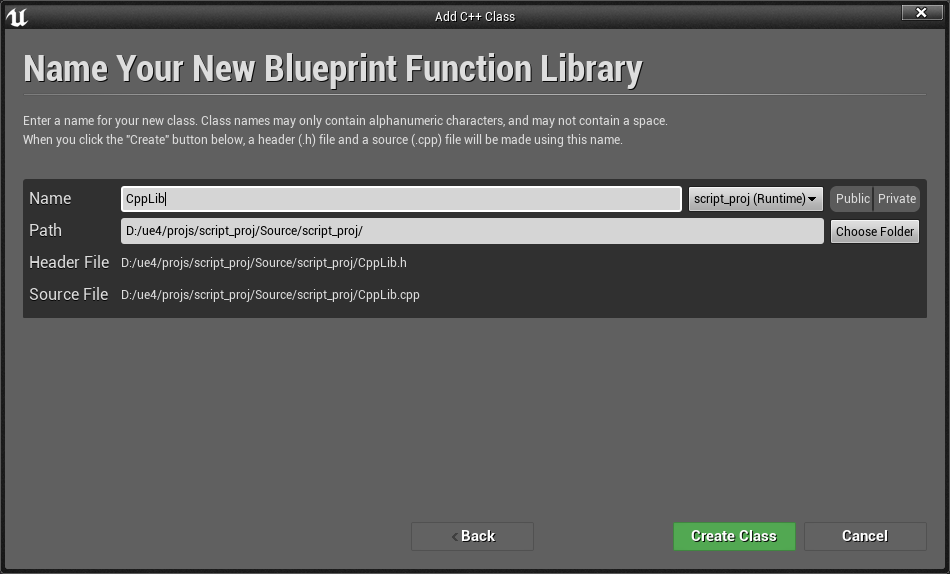
- 修改 .h 文件
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #pragma once #include "CoreMinimal.h" #include "Kismet/BlueprintFunctionLibrary.h" #include "CppLib.generated.h" /** * */ UCLASS() class SCRIPT_PROJ_API UCppLib : public UBlueprintFunctionLibrary { GENERATED_BODY() public: UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static void setFolderColor(FString FolderPath, FLinearColor Color); }; - 修改 .cpp 文件
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #include "CppLib.h" #include "Runtime/Core/Public/Misc/ConfigCacheIni.h" void UCppLib::setFolderColor(FString FolderPath, FLinearColor Color) { GConfig->SetString(TEXT("PathColor"), *FolderPath, *Color.ToString(), GEditorPerProjectIni); } - 在 UE4 中点击重新编译。
在蓝图中设置文件夹颜色
- 创建蓝图类“Folder”。
- 编辑事件节点,编译。
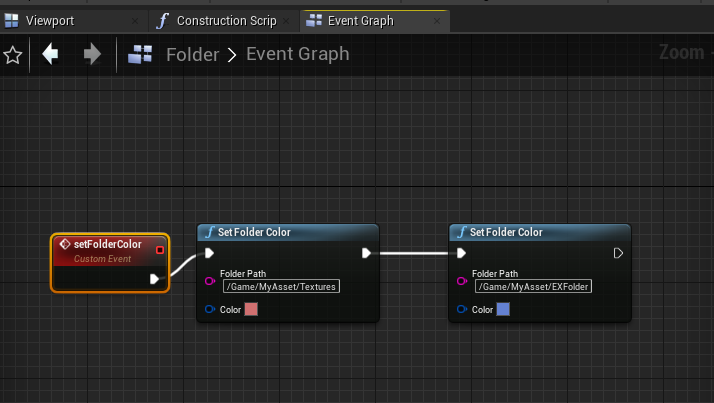
其中,自定义事件节点勾选“Call In Editor”,该事件会显示在属性编辑器上。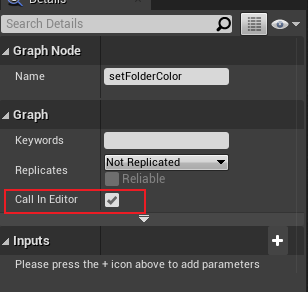
- 在场景中创建“Folder”,点击其属性中的“Set Folder Color”
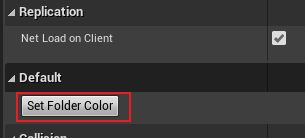
- 创建 “/Game/MyAsset/EXFolder”,可以看到颜色为蓝色,而对已经存在的文件夹颜色修改需要重启后才能看到效果。
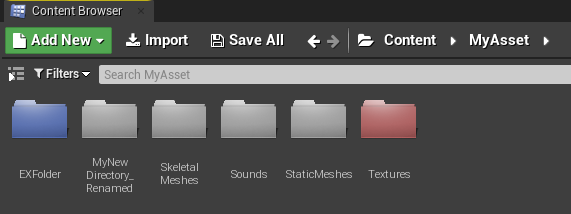
在Python中创建颜色文件夹
AssetFunction_4.py
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
# import AssetFunction_4 as af
# reload(af)
# af.generateColoredDirectories()
def generateColoredDirectories():
for x in range(40, 80):
dir_path = '/Game/MyAsset/MyColorFolder/' + str(x)
linear_color = getGradientColor(x)
unreal.CppLib.set_folder_color(dir_path, linear_color)
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.make_directory(dir_path)
def getGradientColor(x):
x = float(x) / 100
return unreal.LinearColor(x, 1-x, 1-x, 1)在 UE4 运行后,会创建颜色不同的文件夹。
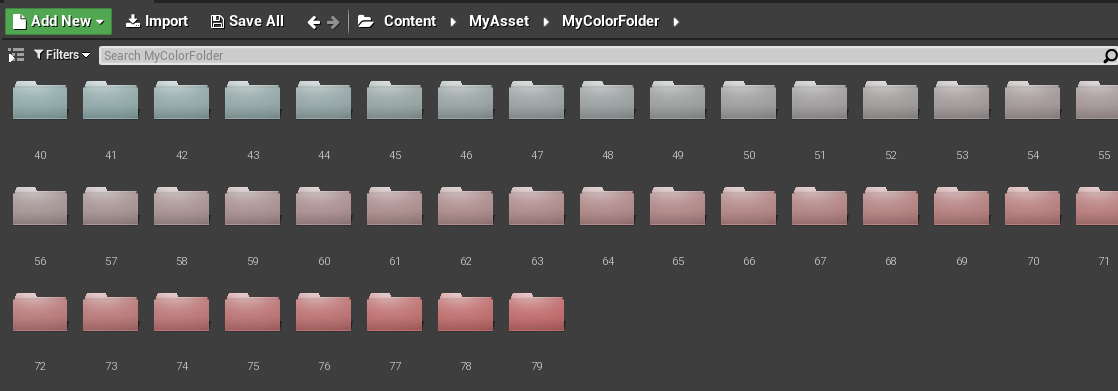
L5 打开和关闭资产
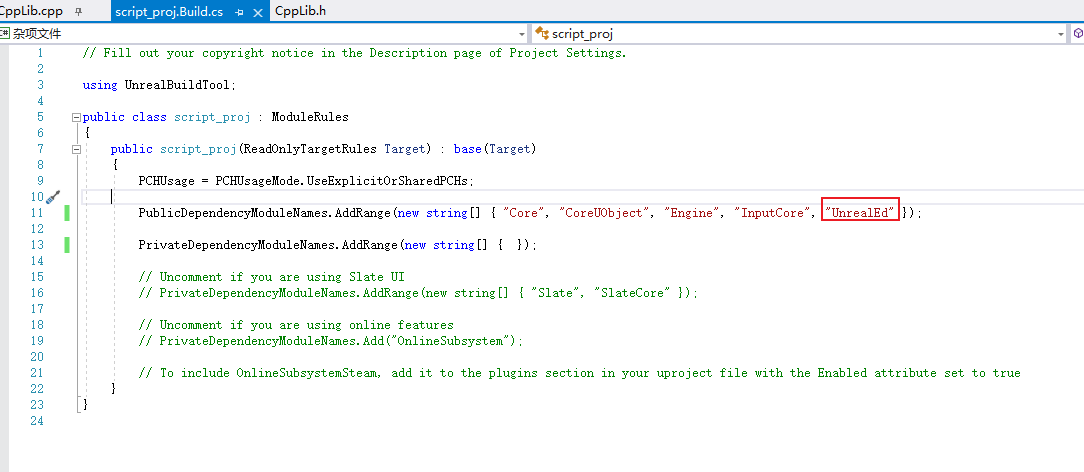
Python只能打开资产,如果要实现关闭资产,需要添加 C++ 类增加功能来实现效果。
添加 build.cs 依赖
CppLib .h 文件代码
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #pragma once #include "CoreMinimal.h" #include "Kismet/BlueprintFunctionLibrary.h" #include "CppLib.generated.h" /** * */ UCLASS() class SCRIPT_PROJ_API UCppLib : public UBlueprintFunctionLibrary { GENERATED_BODY() public: UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static void CloseEditorForAssets(TArray<UObject*> Assets); UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static TArray<UObject*> GetAssetsOpenedInEditor(); };CppLib .cpp 文件代码
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #include "CppLib.h" #include "Editor.h" #include "Editor/UnrealEd/Public/Subsystems/AssetEditorSubsystem.h" void UCppLib::CloseEditorForAssets(TArray<UObject*> Assets) { UAssetEditorSubsystem* AssetEditorSubsystem = GEditor->GetEditorSubsystem<UAssetEditorSubsystem>(); for (UObject* Asset : Assets) { AssetEditorSubsystem->CloseAllEditorsForAsset(Asset); } } TArray<UObject*> UCppLib::GetAssetsOpenedInEditor() { UAssetEditorSubsystem* AssetEditorSubsystem = GEditor->GetEditorSubsystem<UAssetEditorSubsystem>(); TArray<UObject*> EditedAssets = AssetEditorSubsystem->GetAllEditedAssets(); return EditedAssets; }注:教程上用的是 FAssetEditorManager ,但由于版本更新已经不适用,需要替换成 UAssetEditorSubsystem 。
AssetFunction_5.py 文件代码
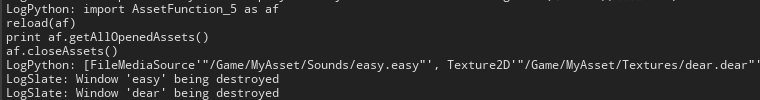
# coding: utf-8 import unreal # ! 加载资产 def openAssets(): assets = [ unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear'), unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Sounds/easy'), unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/StaticMeshes/static_fbx') ] unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().open_editor_for_assets(assets) # ! 获取已经打开的资产列表 def getAllOpenedAssets(): return unreal.CppLib.get_assets_opened_in_editor() # ! 关闭所有打开的资产 def closeAssets(): assets = getAllOpenedAssets() unreal.CppLib.close_editor_for_assets(assets)在 UE4 中调试代码
import AssetFunction_5 as af reload(af) print af.getAllOpenedAssets() af.closeAssets()打印出已经打开的资产窗口,以及关闭所有资产窗口。
L6 选择内容浏览器中的资产
利用 Python 选择指定资产
AssetFunction_6.py
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
# import AssetFunction_6 as af
# reload(af)
# af.showAssetsInContentBrowser()
# ! 选择指定资产
def showAssetsInContentBrowser():
paths = [
'/Game/MyAsset/Sounds/easy',
'/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear'
]
unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.sync_browser_to_objects(paths)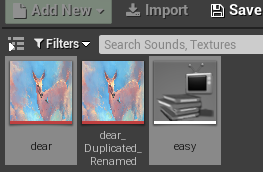
利用 C++ 和 Python 设置选择资产和文件夹
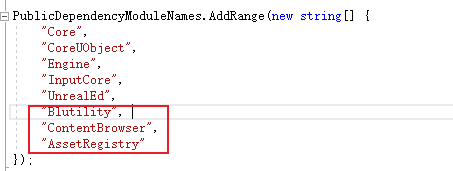
添加 build.cs 依赖
CppLib .h 文件代码
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #pragma once #include "CoreMinimal.h" #include "Kismet/BlueprintFunctionLibrary.h" #include "CppLib.generated.h" /** * */ UCLASS() class SCRIPT_PROJ_API UCppLib : public UBlueprintFunctionLibrary { GENERATED_BODY() public: UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static TArray<FString> GetSelectedAssets(); UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static TArray<FString> GetSelectedFolders(); UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static void SetSelectedAssets(TArray<FString> Paths); UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python") static void SetSelectedFolders(TArray<FString> Paths); };CppLib .cpp 文件代码
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings. #include "CppLib.h" #include "Editor/ContentBrowser/Public/ContentBrowserModule.h" #include "Editor/ContentBrowser/Private/SContentBrowser.h" #include "Runtime/AssetRegistry/Public/AssetRegistryModule.h" TArray<FString> UCppLib::GetSelectedAssets() { FContentBrowserModule& ContentBrowserModule = FModuleManager::LoadModuleChecked<FContentBrowserModule>("ContentBrowser"); // get selected assets TArray<FAssetData> SelectedAssets; ContentBrowserModule.Get().GetSelectedAssets(SelectedAssets); // convert assets to string TArray<FString> Result; for (FAssetData& AssetData : SelectedAssets) { Result.Add(AssetData.PackageName.ToString()); } return Result; } void UCppLib::SetSelectedAssets(TArray<FString> Paths) { FContentBrowserModule& ContentBrowserModule = FModuleManager::LoadModuleChecked<FContentBrowserModule>("ContentBrowser"); FAssetRegistryModule& AssetRegistryModule = FModuleManager::LoadModuleChecked<FAssetRegistryModule>("AssetRegistry"); // convert the string to FName TArray<FName> PathsName; for (FString Path : Paths) { PathsName.Add(*Path); } FARFilter AssetFilter; AssetFilter.PackageNames = PathsName; // Find the assets TArray<FAssetData> AssetDatas; AssetRegistryModule.Get().GetAssets(AssetFilter, AssetDatas); // Ask the ContentBrowser to select them Different to python, the folder levels is also selected. ContentBrowserModule.Get().SyncBrowserToAssets(AssetDatas); } TArray<FString> UCppLib::GetSelectedFolders() { FContentBrowserModule& ContentBrowserModule = FModuleManager::LoadModuleChecked<FContentBrowserModule>("ContentBrowser"); TArray<FString> SelectedFolders; ContentBrowserModule.Get().GetSelectedFolders(SelectedFolders); return SelectedFolders; } void UCppLib::SetSelectedFolders(TArray<FString> Paths) { FContentBrowserModule& ContentBrowserModule = FModuleManager::LoadModuleChecked<FContentBrowserModule>("ContentBrowser"); TArray<FString> SelectedFolders; ContentBrowserModule.Get().SyncBrowserToFolders(Paths); }Python 调用 C++ 测试运行
# ! 调用 C++ 命令设置选择文件夹 def getSelectedAssets(): return unreal.CppLib.get_selected_assets(paths) # ! 调用 C++ 命令设置选择文件夹 def setSelectedAssets(): paths = [ '/Game/MyAsset/Sounds/easy', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear' ] return unreal.CppLib.set_selected_assets(paths) # ! 调用 C++ 命令获取选择文件夹 def getSelectedFolders(): return unreal.CppLib.get_selected_folders() # ! 调用 C++ 命令设置文件夹 def setSelectedFolders(): paths = [ '/Game/MyAsset/Sounds', '/Game/MyAsset/Textures' ] return unreal.CppLib.set_selected_folders(paths)
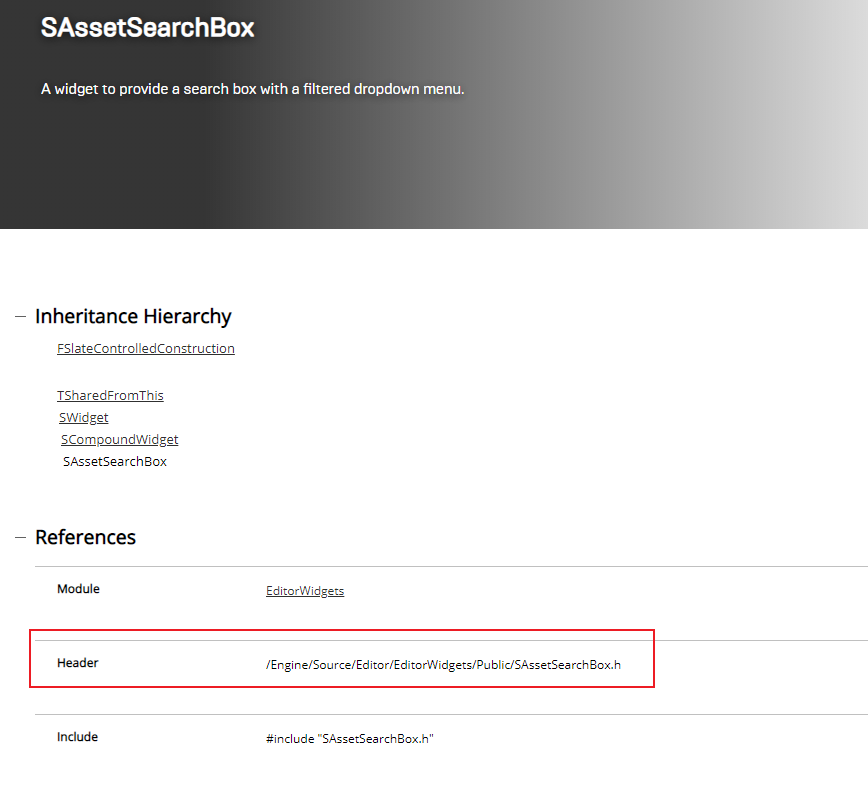
⚠ 令人奇怪的是,在 UE4 中编译测试可以实现我们想要的效果,但是在Visual Studio中却会报错:无法打开源文件 "SAssetSearchBox.h"12 。然鹅在VS2017有小伙伴测试没有报错,不知道是不是版本的问题。
为了解决这个问题,我重新新建了一个项目,把代码重新编译,仍然不通过。我在VS 2019 的项目设置 VC++ 目录的包含目录中添加了一个新路径,在 bulid.cs 文件 PublicDependencyModuleNames.AddRange() 中添加”EditorWidgets”,重新生成项目,成功!😄
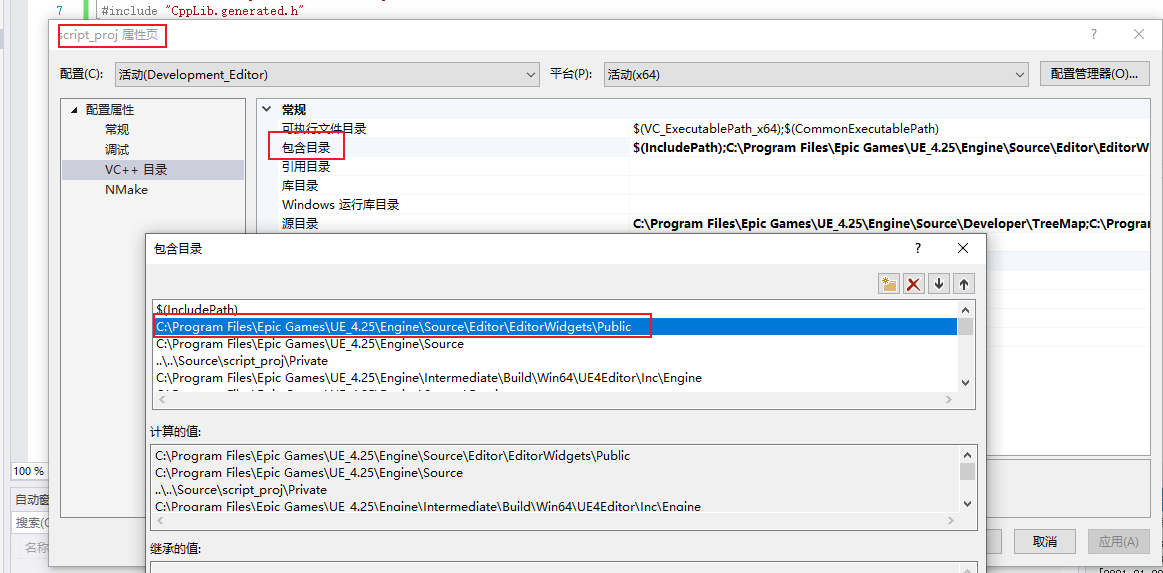
该路径是通过 C++ Api SAssetSearchBox 中找到的。
L7 显示进度条
该部分实现效果为:在 UE4 中显示进度条框并执行相对应任务。
教程中可以完全使用 Python 来实现该功能,但实际测试时发现,当前版本某些方法已经弃用或找不到 Python 接口,如 unreal.EditorCppLib.begin_spawn_actor() 和 unreal.GameplayStatics.finish_spawning_actor()。因此还是结合 C++、Blueprint 以及 Python 实现。
EditorFunction_1.py
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
import random
import time
def executeSlowTask():
quantity_steps_in_slow_task = 10
with unreal.ScopedSlowTask(quantity_steps_in_slow_task, 'My Slow Task Text ...') as slow_task:
slow_task.make_dialog(True)
for x in range(quantity_steps_in_slow_task):
if slow_task.should_cancel():
break
slow_task.enter_progress_frame(1, 'My Slow Task Text ...' + str(x) + ' / ' + str(quantity_steps_in_slow_task))
# Execute slow logic
deferredSpawnActor()
time.sleep(1)
def deferredSpawnActor():
world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world()
# ! blueprint actor
actor_class = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_blueprint_class('/Game/BluePrint/bp_actor')
actor_location = unreal.Vector(random.uniform(0.0, 2000.0), random.uniform(0.0, 2000.0), 0.0)
actor_rotation = unreal.Rotator(random.uniform(0.0, 360.0), random.uniform(0.0, 360.0), random.uniform(0.0, 360.0))
actor_scale = unreal.Vector(random.uniform(0.1, 2.0), random.uniform(0.1, 2.0), random.uniform(0.1, 2.0))
actor_transform = unreal.Transform(actor_location, actor_rotation, actor_scale)
# ! "GameplayStatics.begin_spawning_actor_from_class()" is deprecated. Use BeginDeferredActorSpawnFromClass instead.
# actor = unreal.GameplayStatics.begin_spawning_actor_from_class(world, actor_class, actor_transform)
# unreal.GameplayStatics.finish_spawning_actor(actor, actor_transform)
actor = unreal.EditorCppLib.begin_spawn_actor(world, actor_class, actor_transform)
unreal.EditorCppLib.finish_spawn_actor(actor, actor_transform)EditorCppLib.h
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#pragma once
#include "CoreMinimal.h"
#include "Kismet/BlueprintFunctionLibrary.h"
#include "EditorCppLib.generated.h"
/**
*
*/
UCLASS()
class SCRIPT_PROJ_API UEditorCppLib : public UBlueprintFunctionLibrary
{
GENERATED_BODY()
public:
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static AActor* BeginSpawnActor(const UObject* WorldContextObj,TSubclassOf < AActor > ActorClass, const FTransform& SpawnTransform);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static void FinishSpawnActor(AActor* MyActor, const FTransform& SpawnTransform);
};EditorCppLib.cpp
// Fill out your copyright notice in the Description page of Project Settings.
#include "EditorCppLib.h"
#include "Runtime/Engine/Classes/Kismet/GameplayStatics.h"
AActor* UEditorCppLib::BeginSpawnActor(const UObject* WorldContextObj, TSubclassOf < AActor > ActorClass, const FTransform& SpawnTransform) {
return UGameplayStatics::BeginDeferredActorSpawnFromClass(WorldContextObj, ActorClass, SpawnTransform);
}
void UEditorCppLib::FinishSpawnActor(AActor* MyActor, const FTransform& SpawnTransform) {
UGameplayStatics::FinishSpawningActor(MyActor, SpawnTransform);
}在 C++ API 中可以查到函数需要的参数及类型。


L8 获取物体属性
利用 C++ 获取类的所有属性名,再用 Python 获取属性值。
CppLib.h文件
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static TArray<FString> GetAllProperties(UClass* Class);CppLib.cpp文件
TArray<FString> UCppLib::GetAllProperties(UClass* Class) {
TArray<FString> Ret;
if (Class != nullptr) {
for (TFieldIterator<UProperty> It(Class); It; ++It) {
UProperty* Property = *It;
if (Property->HasAnyPropertyFlags(EPropertyFlags::CPF_Edit)) {
Ret.Add(Property->GetName());
}
}
}
return Ret;
}PythonHelpers.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
def getAllProperties(object_class):
return unreal.CppLib.get_all_properties(object_class)
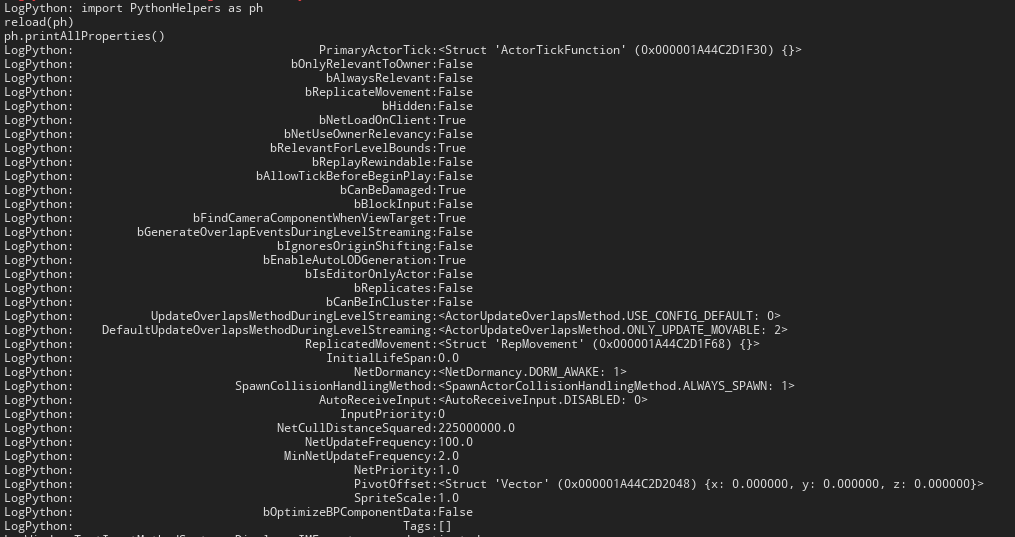
def printAllProperties():
obj = unreal.Actor()
object_class = obj.get_class()
for x in getAllProperties(object_class):
name = x
while len(name) < 50:
name = ' ' + name
print name + ':' + str(obj.get_editor_property(x))效果展示:
L9 运行 Cmd
使用 Python 和 C++ 在 UE4 中运行 Cmd 指令。
CppLib.h文件
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static void ExecuteConsoleCommand(FString ConsoleCommand);CppLib.cpp文件
需要在cs文件中添加依赖项 “UnrealEd” -> PublicDependencyModuleNames)
#include "Editor/UnrealEd/Public/Editor.h"
void UCppLib::ExecuteConsoleCommand(FString ConsoleCommand) {
if (GEditor) {
UWorld* World = GEditor->GetEditorWorldContext().World();
if (World) {
GEditor->Exec(World, *ConsoleCommand, *GLog);
}
}
}EditorFunction_2.py文件
def executeConsoleCommand():
console_commands = ['r.ScreenPercentage 0.1', 'r.Color.Max 6', 'stat fps', 'stat unit']
for x in console_commands:
unreal.CppLib.execute_console_command(x)运行效果: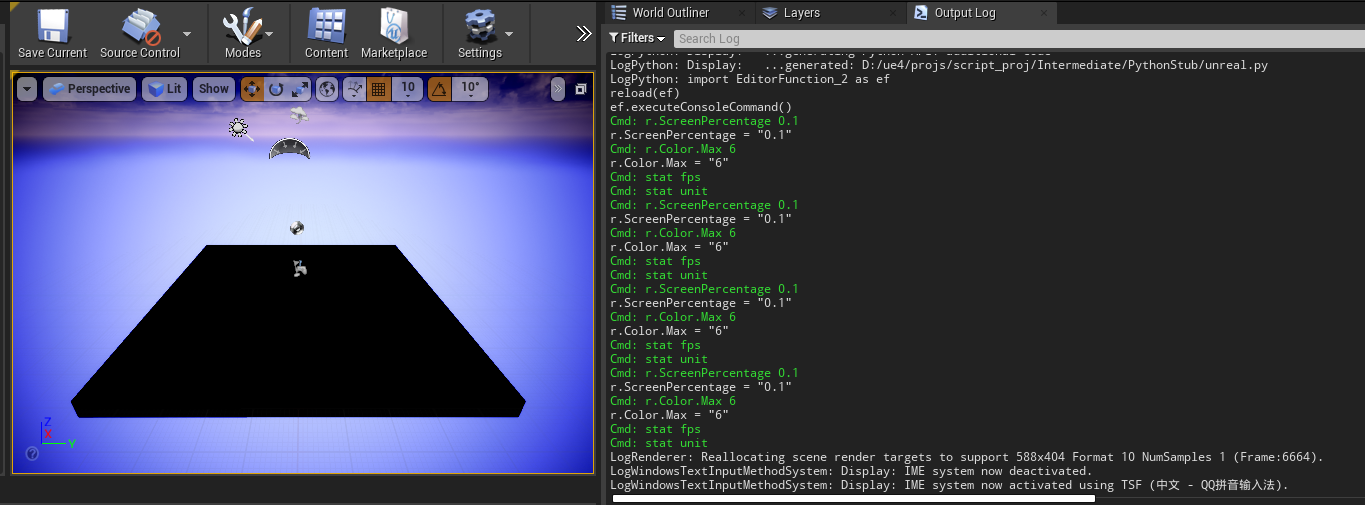
L10 在场景中实例化 Actor
在 Python 中可以使用 unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.spawn_actor_from_class(actor_class, actor_location, actor_rotation) 进行实例化 Actor 。
WorldFunctions.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
def spawnActor():
actor_class = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_blueprint_class('/Game/BluePrint/MyActor')
actor_location = unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
actor_rotation = unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.spawn_actor_from_class(actor_class, actor_location, actor_rotation)
def deferredSpawnActor():
world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world()
actor_class = unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.load_blueprint_class('/Game/BluePrint/MyActor')
actor_location = unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
actor_rotation = unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
actor_scale = unreal.Vector(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)
actor_transform = unreal.Transform(actor_location, actor_rotation, actor_scale)
actor = unreal.EditorCppLib.begin_spawn_actor(world, actor_class, actor_transform)
actor_tags = actor.get_editor_property('tags')
actor_tags.append('My Python Tag')
actor.set_editor_property('tag', actor_tags)
unreal.EditorCppLib.finish_spawn_actor(actor, actor_transform) 为了更直观看到实例化过程,我们可以对蓝图 Actor 进行编辑并对节点连接,使得在实例化时会打印出内容。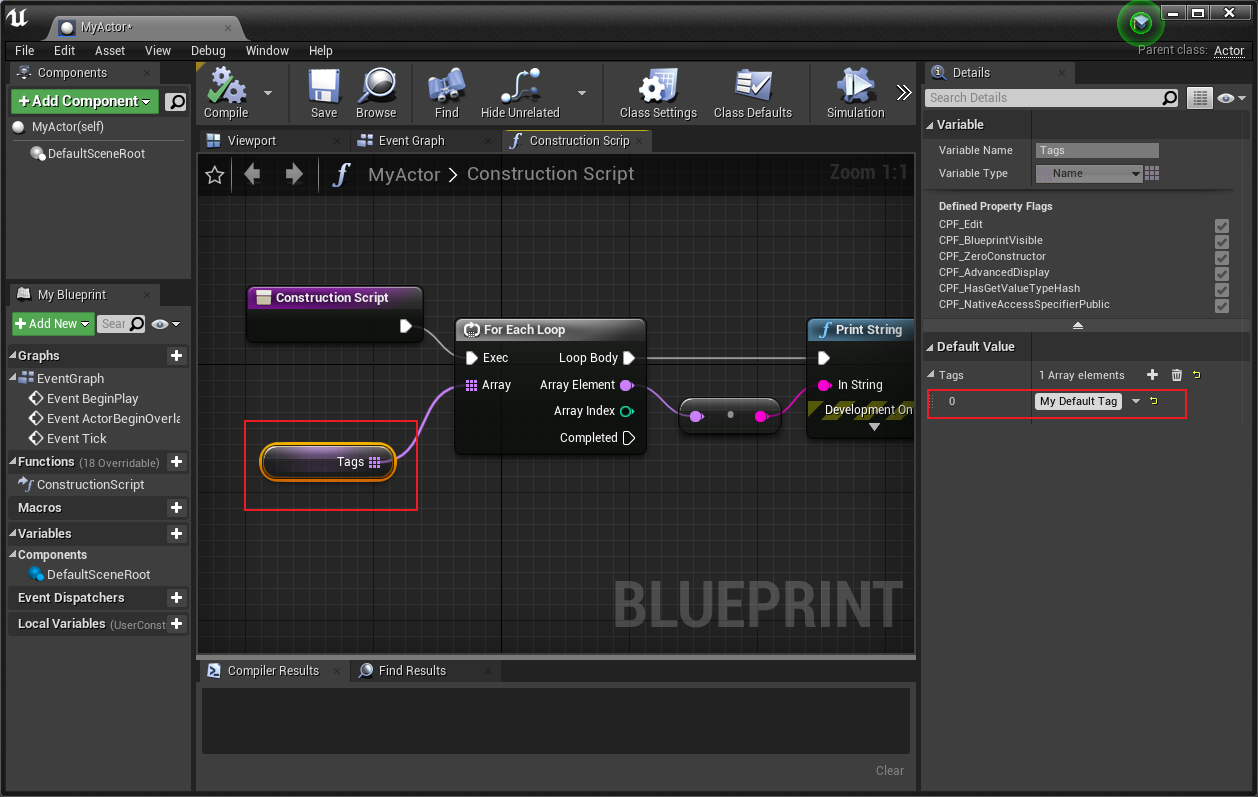
在 UE4 中运行效果:
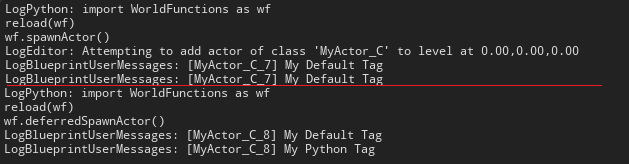
可以看到,使用 unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.spawn_actor_from_class() 时,虽然只创建了一次物体但实例化了两次,而后面的方法只实例化了一次。
L11 类型转换
如果使用 Python 进行类型转换,转换不支持的类型时会引起崩溃,可以用 C++ 进行类型转换判断。
PythonHelpers_2.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
def tryCast():
# ! this run crash use python
# if unreal.Actor.cast(unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear')):
if unreal.Texture2D.cast(unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear')):
print 'Cast Succeeded'
else:
print 'Cast Failed'
def castObject():
# ! this will not crash user C++
if cast(unreal.load_asset('/Game/MyAsset/Textures/dear'), unreal.Actor):
print 'Cast Succeeded'
else:
print 'Cast Failed'
def cast(object_to_cast, object_class):
try:
return object_class.cast(object_to_cast)
except:
return NoneL12 获取世界中的指定Actor
有三种方法筛选Actor:
- 获取选择的Actor:unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_selected_level_actors()
- 通过类型获取: unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class()
- 通过 tag 获取: unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class()
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
def getSelectedActors():
# ! Selected
selected_actors = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_selected_level_actors()
return selected_actors
def getClassActors(actor_class):
# ! Class
world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world()
class_actors = unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(world, actor_class)
return class_actors
def getTagActors(actor_tag):
# ! Tag
world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world()
tag_actors = unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_with_tag(world, actor_tag)
return tag_actors
def getAllActors():
# ! All
world = unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world()
all_actors = unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(world, unreal.Actor)
return all_actors
def sortActors(use_selection = False, actor_class = None, actor_tag = None):
"""如果有指定,则筛选指定 Actors。否则返回全部 Actors
"""
# ! return all actors
if not use_selection and not actor_class and not actor_tag:
return getAllActors()
# ! get sort actors
selected_actors, class_actors, tag_actors = [], [], []
if use_selection:
selected_actors = list(getSelectedActors())
if actor_class:
class_actors = list(getClassActors(actor_class))
if actor_tag:
tag_actors = list(getTagActors(actor_tag))
final_actors = selected_actors + class_actors + tag_actors
for actor in final_actors:
if use_selection and actor in selected_actors:
pass
else:
final_actors.remove(actor)
continue
if actor_class and actor in class_actors:
pass
else:
final_actors.remove(actor)
continue
if actor_tag and actor in tag_actors:
pass
else:
final_actors.remove(actor)
continue
if final_actors:
return final_actors
else:
return getAllActors()
def cast(object_to_cast, object_class):
try:
return object_class.cast(object_to_cast)
except:
return getAllActors()写这个的时候,发现获取出来的 Actors 存储都是用的 数组 array,虽然方法有些和列表 List 相同,但是使用起来效果不一样,最终打印结果数组显示和数组内元素显示有差异。

L13 使用 Qt 进行界面开发
在 UE 中一样可以使用Qt Designer进行界面开发。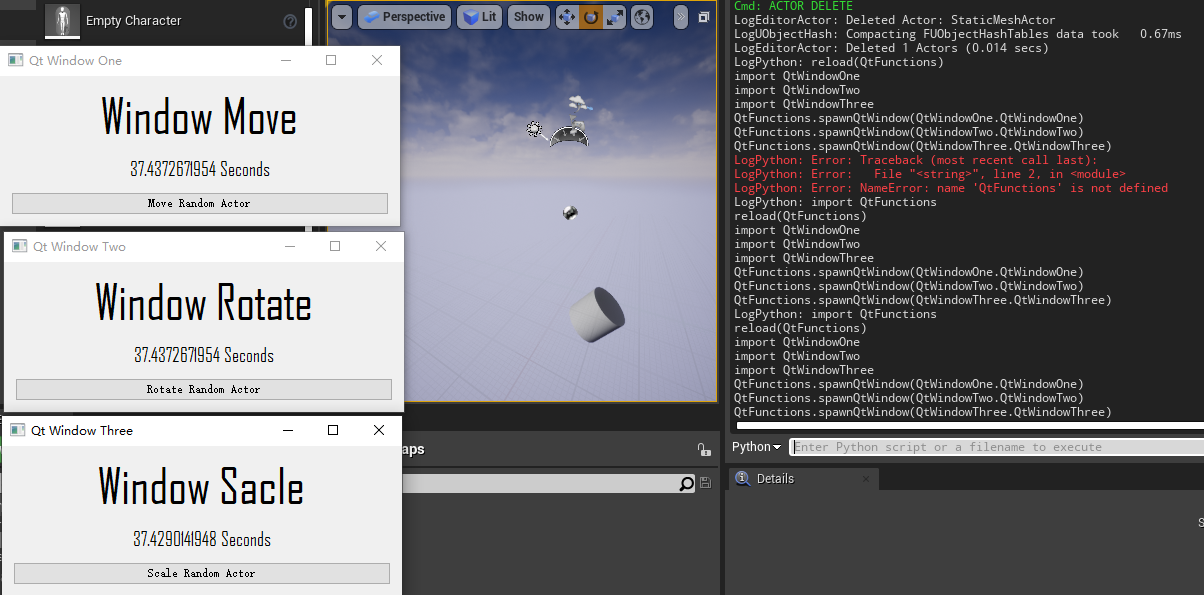
主函数 QtFunctions
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
import sys
sys.path.append('C:/Python27/Lib/site-packages')
from PySide import QtGui
def __QtAppTick__(delta_seconds):
for window in opened_windows:
window.eventTick(delta_seconds)
def __QtAppQuit__():
unreal.unregister_slate_post_tick_callback(tick_handle)
def __QtWindowClosed__(window=None):
if window in opened_windows:
opened_windows.remove(window)
unreal_app = QtGui.QApplication.instance()
if not unreal_app:
unreal_app = QtGui.QApplication(sys.argv)
tick_handle = unreal.register_slate_post_tick_callback(__QtAppTick__)
unreal_app.aboutToQuit.connect(__QtAppQuit__)
existing_windows = {}
opened_windows = []
def spawnQtWindow(desired_window_class=None):
window = existing_windows.get(desired_window_class, None)
if not window:
window = desired_window_class()
existing_windows[desired_window_class] = window
window.aboutToClose = __QtWindowClosed__
if window not in opened_windows:
opened_windows.append(window)
window.show()
window.activateWindow()实现位移函数 QtWindowOne
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
import os
import sys
sys.path.append('C:/Python27/Lib/site-packages')
from PySide.QtGui import *
from PySide import QtUiTools
WINDOW_NAME = 'Qt Window One'
UI_FILE_FULLNAME = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'ui', 'window_move.ui').replace('\\','/')
class QtWindowOne(QWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super(QtWindowOne, self).__init__(parent)
self.aboutToClose = None
self.widget = QtUiTools.QUiLoader().load(UI_FILE_FULLNAME)
self.widget.setParent(self)
self.setWindowTitle(WINDOW_NAME)
self.setGeometry(100, 100, self.widget.width(),self.widget.height())
self.initialiseWidget()
def clossEvent(self, event):
if self.aboutToClose:
self.aboutToClose(self)
event.accept()
def eventTick(self, delta_seconds):
self.myTick(delta_seconds)
def initialiseWidget(self):
self.time_while_this_window_is_open = 0.0
self.random_actor = None
self.random_actor_is_going_up = True
self.widget.pushButton.clicked.connect(self.moveRandomActorInScene)
def moveRandomActorInScene(self):
import random
import WorldFunctions_2
all_actors = WorldFunctions_2.sortActors(use_selection=False, actor_class=unreal.StaticMeshActor, actor_tag=None)
rand = random.randrange(0, len(all_actors))
self.random_actor = all_actors[rand]
def myTick(self, delta_seconds):
self.time_while_this_window_is_open += delta_seconds
self.widget.label.setText("{} Seconds".format(self.time_while_this_window_is_open))
if self.random_actor:
actor_location = self.random_actor.get_actor_location()
speed = 300.0 * delta_seconds
if self.random_actor_is_going_up:
if actor_location.z > 1000.0:
self.random_actor_is_going_up = False
else:
speed = -speed
if actor_location.z < 0.0:
self.random_actor_is_going_up = True
self.random_actor.add_actor_world_offset(unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, speed), False, False)实现旋转函数(部分) QtWindowTwo
def myTick(self, delta_seconds):
self.time_while_this_window_is_open += delta_seconds
self.widget.label.setText("{} Seconds".format(self.time_while_this_window_is_open))
if self.random_actor:
speed = 90.0 * delta_seconds
self.random_actor.add_actor_world_rotation(unreal.Rotator(0.0, 0.0, speed), False, False)实现缩放函数(部分) QtWindowThree
def myTick(self, delta_seconds):
self.time_while_this_window_is_open += delta_seconds
self.widget.label.setText("{} Seconds".format(self.time_while_this_window_is_open))
if self.random_actor:
actor_scale = self.random_actor.get_actor_scale3d()
speed = 3.0 * delta_seconds
if self.random_actor_is_going_up:
if actor_scale.z > 2.0:
self.random_actor_is_going_up = False
else:
speed = -speed
if actor_scale.z < 0.5:
self.random_actor_is_going_up = True
self.random_actor.set_actor_scale3d(unreal.Vector(actor_scale.x + speed, actor_scale.y + speed, actor_scale.z + speed))L14 git 代码
emmm,学习到这里,才看到作者把代码放到 git 上了。-> UnrealPythonLibrary
不用全部自己手打可以节省更多时间!
不过有些代码自己还会做一些修改,自己的代码也放到 git上了 -> UnrealPythonStudy
L15 在世界中选择和取消选择物体
获取选择物体:unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_selected_level_actors()
设置选择物体:unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.set_selected_level_actors(actors_to_select)
WorldFunctions_3.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
# return: obj List unreal.Actor : The selected actors in the world
def getSelectedActors():
return unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_selected_level_actors()
# Note: Will always clear the selection before selecting.
# actors_to_select: obj List unreal.Actor : The actors to select.
def selectActors(actors_to_select=[]):
unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.set_selected_level_actors(actors_to_select)
def selectActors_EXAMPLE():
import WorldFunctions_2
all_actors = WorldFunctions_2.sortActors()
actors_to_select = []
for x in range(len(all_actors)):
if x % 2:
actors_to_select.append(all_actors[x])
selectActors(actors_to_select)
def clearActorSelection_EXAMPLE():
selectActors()L16 在视口中聚焦物体
可以实现在全部/活跃视口中聚焦指定物体。
EditorFunction_3.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
import random
# active_viewport_only: bool : If True, will only affect the active viewport
# actor: obj unreal.Actor : The actor you want to snap to
def focusViewportOnActor(active_viewport_only=True, actor=None):
# ! focus command
command = 'CAMERA ALIGN'
if active_viewport_only:
command += ' ACTIVEVIEWPORTONLY'
if actor:
command += ' NAME=' + actor.get_name()
unreal.CppLib.execute_console_command(command)
def focusAllViewportsOnSelectedActors_EXAMPLE():
focusViewportOnActor(False)
def focusActiveViewportOnRandomActor_EXAMPLE():
actors_in_world = unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world(), unreal.Actor)
random_actor_in_world = actors_in_world[random.randrange(len(actors_in_world))]
focusViewportOnActor(True, random_actor_in_world)L17 移动、旋转视口
结合 C++ 和 snapViewport 实现。
C++ .h 文件(部分)
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static void SetViewportLocationAndRotation(int ViewportIndex, FVector Location, FRotator Rotation);
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static int GetActiveViewportIndex();C++ .cpp 文件(部分)
void UCppLib::SetViewportLocationAndRotation(int ViewportIndex, FVector Location, FRotator Rotation) {
if (GEditor != nullptr && ViewportIndex < GEditor->GetLevelViewportClients().Num()) {
FLevelEditorViewportClient* LevelViewportClient = GEditor->GetLevelViewportClients()[ViewportIndex];
if (LevelViewportClient != nullptr) {
LevelViewportClient->SetViewLocation(Location);
LevelViewportClient->SetViewRotation(Rotation);
}
}
}
int UCppLib::GetActiveViewportIndex() {
int Index = 1;
if (GEditor != nullptr && GCurrentLevelEditingViewportClient != nullptr) {
GEditor->GetLevelViewportClients().Find(GCurrentLevelEditingViewportClient, Index);
}
return Index;
}Python EditorFunction_4.py 文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
import random
# return: int : The index of the active viewport
def getActiveViewportIndex():
return unreal.CppLib.get_active_viewport_index()
# viewport_index: int : The index of the viewport you want to affect
# location: obj unreal.Vector : The viewport location
# rotation: obj unreal.Rotator : The viewport rotation
def setViewportLocationAndRotation(viewport_index=1, location=unreal.Vector(), rotation=unreal.Rotator()):
unreal.CppLib.set_viewport_location_and_rotation(viewport_index, location, rotation)
# viewport_index: int : The index of the viewport you want to affect
# actor: obj unreal.Actor : The actor you want to snap to
def snapViewportToActor(viewport_index=1, actor=None):
setViewportLocationAndRotation(viewport_index, actor.get_actor_location(), actor.get_actor_rotation())
def setViewportLocationAndRotation_EXAMPLE():
viewport_index = getActiveViewportIndex()
setViewportLocationAndRotation(viewport_index, unreal.Vector(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), unreal.Rotator(0.0, 90.0, 0.0))
def snapViewportToActor_EXAMPLE():
actors_in_world = unreal.GameplayStatics.get_all_actors_of_class(unreal.EditorLevelLibrary.get_editor_world(), unreal.Actor)
random_actor_in_world = actors_in_world[random.randrange(len(actors_in_world))]
viewport_index = getActiveViewportIndex()
snapViewportToActor(viewport_index, random_actor_in_world)L18 创建 generic 资产
AssetFunction_7.py文件
# coding: utf-8
import unreal
def createGenericAsset(asset_path='', unique_name=True, asset_class=None, asset_factory=None):
if unique_name:
asset_path, asset_name = unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().create_unique_asset_name(base_package_name=asset_path, suffix='')
if not unreal.EditorAssetLibrary.does_asset_exist(asset_path=asset_path):
path = asset_path.rsplit('/', 1)[0]
name = asset_path.rsplit('/', 1)[1]
return unreal.AssetToolsHelpers.get_asset_tools().create_asset(asset_name=name, package_path=path, asset_class=asset_class, factory=asset_factory)
return unreal.load_asset(asset_path)
def createGenericAsset_EXAMPLE():
base_path = '/Game/MyAsset/GenericAssets/'
generic_assets = [
[base_path + 'sequence', unreal.LevelSequence, unreal.LevelSequenceFactoryNew()],
[base_path + 'material', unreal.Material, unreal.MaterialFactoryNew()],
[base_path + 'world', unreal.World, unreal.WorldFactory()],
[base_path + 'particle_system', unreal.ParticleSystem, unreal.ParticleSystemFactoryNew()],
[base_path + 'paper_flipbook', unreal.PaperFlipbook, unreal.PaperFlipbookFactory()],
[base_path + 'data_table', unreal.DataTable, unreal.DataTableFactory()], # Will not work
]
for asset in generic_assets:
print createGenericAsset(asset[0], True, asset[1], asset[2])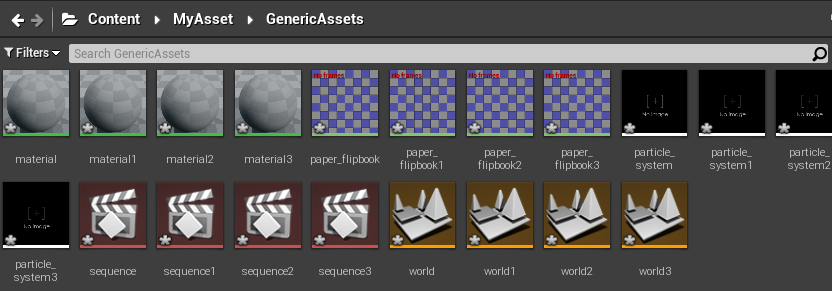
L19 添加动画序列
pass
L20 利用 Blueprint 运行Python代码
原理和利用 Blueprint 运行 cmd 代码相同。
build.cs 加上 “Python”, “PythonScriptPlugin”
C++ .h(部分)
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, Category = "Unreal Python")
static void ExecutePythonScript(FString PythonScript);C++ .cpp(部分)
#include "../Plugins/Experimental/PythonScriptPlugin/Source/PythonScriptPlugin/Private/PythonScriptPlugin.h"
void UCppLib::ExecutePythonScript(FString PythonScript) {
FPythonScriptPlugin::Get()->ExecPythonCommand(*PythonScript);
}蓝图节点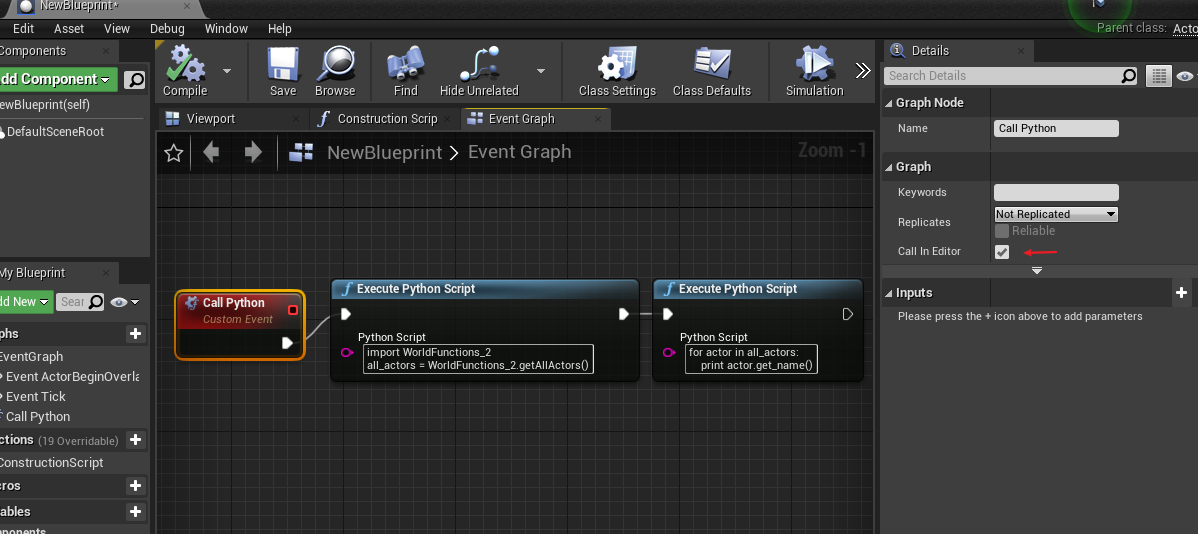
点击事件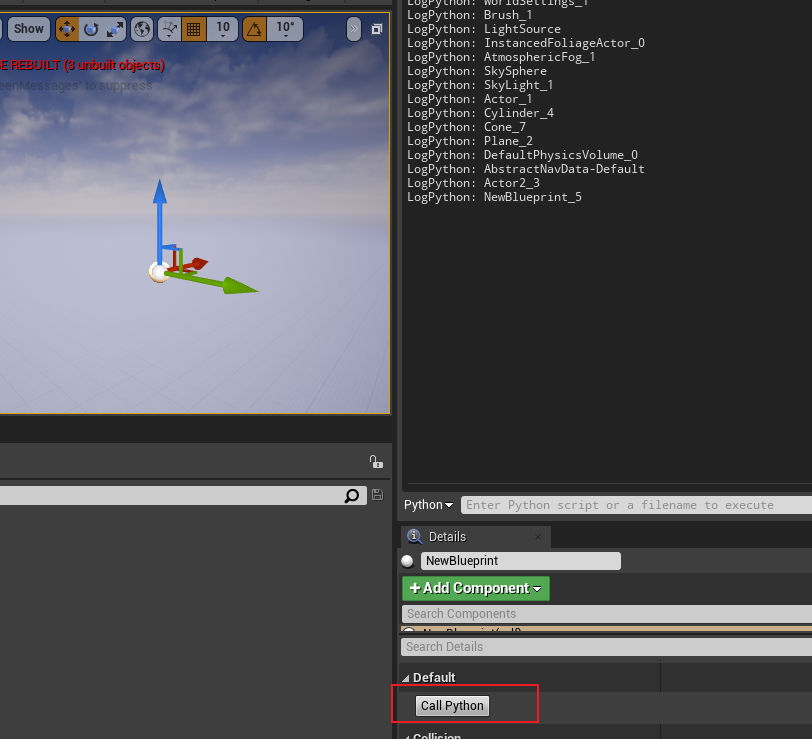
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!